DECODING JAIPURŌĆÖS
DIGITAL PAYMENTS LANDSCAPE
By Catalyst Communications Team, May 2017
Research Partners
The last few months have been a watershed for the digital payments space in India. With concerted efforts from the government, as well as businesses, the landscape has seen some tectonic developments. From mobile wallets to lower cost, interoperable solutions such as UPI, Bharat QR code and Aadhar Pay, more tailor-made solutions to meet specific needs of small businesses and mass consumer segments are now seen on the horizon. Moreover, with the government announcing a budget of Rs. 495 crore to promote digital transactions using BHIM (a UPI enabled app), with a target to catalyze 25 billion digital transactions in the fiscal year ending March 2018, policy and market forces are colluding to promote a less cash economy. However, despite recent advancements, the consumption spends using digital means currently stand at a dismal 51%, making it crucial to investigate the reasons for low solution adoption.
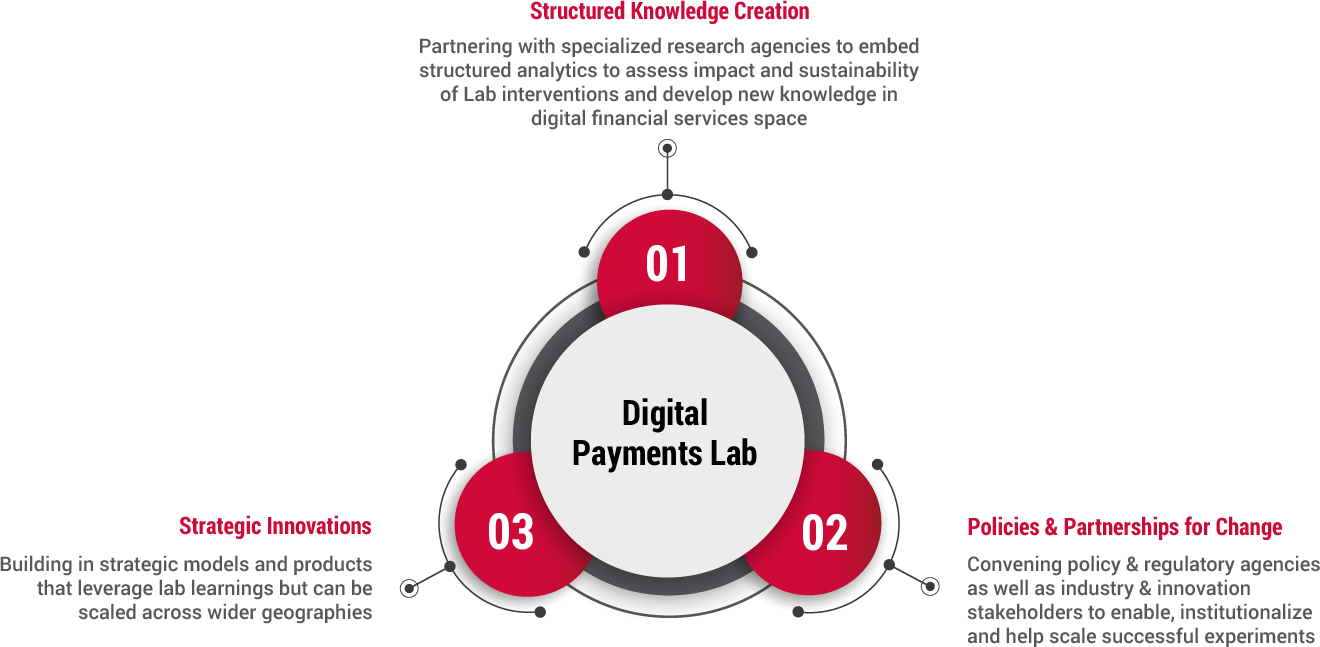
For India to accelerate its progress towards a less cash economy, there is a clear need to deliberate on economic, social and behavioral dependencies that steer the decision of the low-income population to adopt digital transactions. In that context, Catalyst, an initiative to accelerate adoption of digital payments in India, has formed strategic partnerships with research organisations such as People Research on IndiaŌĆÖs Consumer Economy (PRICE), IFMR LEAD, CEGA and Ideas 42. Bringing in strong research expertise and rich insights to bear on Catalyst initiatives, these partnerships will play a substantive role in guiding CatalystŌĆÖs engagements with operational partners to design and implement a range of needs-based payment solutions for the ŌĆ£last mileŌĆØ. They will help us get a deeper understanding on how merchants and consumers interact with financial tools, what are the barriers and what are the value propositions that induce them to transact digitally
Jaipur, CatalystŌĆÖs first Digital Payment Lab
Adopting a unique ecosystem approach defined by local geography, Catalyst has operationalized its very first digital payments lab in Jaipur - a tier 2 city with a 3 million plus population, more than 200,000 commercial establishments, and over 75,000 informal establishments including home based and roving businesses. Using new technologies, business models, and institutional innovations, combined with rigorous research evidence, Catalyst aims to build an inclusive digital financial ecosystem in Jaipur - one that is demand-driven, accessible and serves as a foundation for greater financial inclusion. Our goal is to create a template for implementing similar initiatives in other cities.
Before embarking on this challenging journey to transform Jaipur into a less cash economy, we immersed ourselves in the current financial and socio-economic landscape of Jaipur, and particularly focused on understanding merchant perspectives towards digital payments. The Sixth Economic Census conducted in Rajasthan (May-June2013), as well as the ŌĆśJaipur Population ProfileŌĆÖ study conducted by PRICE, helped us in getting an understanding of the city across various themes, such as income segments, occupational categories, bank penetration, expenditure, saving, investments and use of digital technologies. In addition to providing an overview of the income segments of Jaipur, which is critical for solution design and implementation, the latter also enabled us to assess the digital readiness in communities, looking into different aspects of technology ŌĆō particularly, access, usage and prevalent infrastructure. Insights from these two studies have underpinned further exploratory initiatives to decode the market dynamics of Jaipur city.
1 Goverment of India (December, 2016), Report on Medium Term Recommendations to Strengthen Digital Payments Ecosystem,
JAIPUR CITY | KEY FEATURES & TRENDS
83% of households in Jaipur fall within the income bracket of <= INR 25000, which is CatalystŌĆÖs core target population. Casual wage labour, shop owners and grade 4 employees (peon, driver, carpenter etc.) are the 3 key occupational categories, that represent 80% of households in the city.
WHEN IS CASH THE FIRST PREFERENCE?
Irrespective of the income group, cash is the preferred choice for transactions, across categories.
Groceries at Store
98% cash
Clothing, Footwear etc.
100% cash
Utility Bills
100% cash
Fuel for Vehicle
100% cash
Durable Goods
98% cash
Restaurants
100% cash
Tours & Travel
100% cash
Recreation
100% cash
DEBT SITUATION
Overall, data indicates low debt penetration in Jaipur city. However, it is important to note that out of the pool of indebted households, most had resorted to informal sources for credit needs. This could indicate barriers for low-income households to secure loans from formal financial institutions.
Source: ICE 360┬░ Survey (2016), PRICE
TYPES OF BUSINESS ESTABLISHMENTS IN JAIPUR AND THEIR FINANCING SOURCES
Source: Sixth Economic Census (2016), CSO
ASSESSING URBAN JAIPURŌĆÖS DIGITAL READINESS
Source: ICE 360┬░ Survey (2016), PRICE
DIGITAL READINESS AND PURPOSE OF INTERNET ACCESS AMONG THE LOW INCOME SEGMENT
Source: ICE 360┬░ Survey (2016), PRICE
SMALL MERCHANTS, WITH A BIG ROLE IN INDIAŌĆÖS DIGITAL PAYMENTS JOURNEY
At Catalyst, we believe that the shift from cash to digital, within local economies, is incumbent on transformation of 3 key stakeholders ŌĆō suppliers, merchants and consumers. Each need to find adequate avenues and incentives for usage of digital payments, creating the need for an approach that focuses on enabling all three forces with requisite payment solutions.
Small merchants, currently with a digital payment penetration of only 6% of the total merchant base in India, serve as an important touchpoint for consumers as well as suppliers. They collectively have immense potential to accelerate the usage and adoption of digital payments. If merchants find transacting digitally beneficial to their businesses and are equipped with need based solutions, they will advocate the use of digital payments to a large consumer base, and also assert the message to suppliers. At the same time, there is a need for coordinated initiatives targeting consumers and suppliers directly, thereby integrating the entire value chain into a digital payment ecosystem.
Recognising the central role of merchants in transforming a city into a less-cash economy, CatalystŌĆÖs first step towards understanding the current trends of digital payments in Jaipur was to interact closely with the small merchants of the city. In doing so, Catalyst partnered IFMR LEAD to conduct an observational survey of 30 markets in Jaipur, out of which 10 markets were selected based on criteria such as presence of low-middle income consumer base, overall size and merchant mix, and current digital payment system penetration. Further, in each market, a random sample covering 25% of the merchant base was surveyed to assess needs and capture merchantsŌĆÖ perspective towards adopting and accepting digital payments from their consumers.
GETTING THE ŌĆ£DIGITAL’┐Į? PULSE OF JAIPUR MARKETS
Low digital payment penetration
To get a comprehensive sense of the current extent of digital penetration in Jaipur city, the study looked at trends in the tourist-centric markets within the walled area of the city, and general residential consumer-centric markets outside the walled area. It is surprising to note that despite having the enabling infrastructure, merchants within the walled city, who primarily cater to tourists, display digital penetration of as low as 11.6%. In contrast, digital payment penetration outside the walled city stands at 20.7%. Overall, penetration of digital payments among merchants in Jaipur, across 10 major markets, is 17%.
Optimistic figures on availability of enabling infrastructure
The study identified power supply, phone network connectivity and access to Internet, as significant factors that affect the digital payment penetration in markets. The numbers on most parameters are encouraging to accelerate usage of digital payments in Jaipur markets. However, a possible roadblock we should take cognizance of is the low penetration of Internet among the merchant base, with only 51% reporting access. This further becomes relevant, as the analysis brought forth high dependence on Internet access for merchants to adopt digital payment methods. Access to Internet increases the probability of going digital by 2.5 times.
Among merchants with Internet access, mobile phones are predominantly used to access the Internet in the business.
57% of merchants use smartphones. Further indicating opportunities to push mobile payment solutions, such as UPI enabled apps.
Access to key infrastructure at market area, for digital payment usage
Number of ATMs in the market area, positively correlate with digital payment penetration
In addition to the dependence on other infrastructural support, high presence of ATMs in a market came to fore as an important contributor to digital payment penetration in that area. This supports the premise that greater access to Cash-in/Cash-out points in a market increases digital payment uptake and usage in that area.
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
OVERALL, JAIPUR BOASTS OF HIGH PENETRATION OF BANK ACCOUNTS WITHIN ITS MERCHANT BASE.
HOWEVER, IN TERMS OF ACTIVE USAGE OF BANK ACCOUNT BY MERCHANTS, AND LINKAGE OF BANK ACCOUNTS WITH SMARTPHONES, THE FIGURES ARE COMPARATIVELY LOW IN MOST MARKETS.
Our study indicated that merchantsŌĆÖ readiness to adopt and use digital payments significantly depends on them having a bank account, its linkage to a mobile phone, and the linkage of the account with the merchantŌĆÖs Aadhaar number. Moreover, an active bank account adds to the probability of a merchantŌĆÖs willingness to adopt digital payments.
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
Probability of using digital payment systems increases by 25 times if the merchant is an active bank account user
WHAT WE LEARNT ABOUT DIGITAL MERCHANTS IN JAIPUR
WHAT ARE THE MOST PREFERRED DIGITAL PAYMENT SOLUTIONS AMONGST MERCHANTS?
Mobile and POS machines are the most widely used digital payment solutions in Jaipur markets. Further, in terms of usage, on an average, a POS machine is used 6.58 times in a day, and Mobile wallets reported usage of 3.28 times a day.
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
WHAT WERE THE TRIGGERS FOR ADOPTION?
Customer retention, Convenience of transactions
Convenience of keeping records, Lesser risk perception with instant credit to wallets
DOES THE PREFERENCE FOR DIGITAL PAYMENT TOOL VARY BASED ON MERCHANT BUSINESS TYPE?
Merchants trading in specialty products such as mobile phones, apparels, bags etc. were largely found to be using POS machines. This is grounded in the fact that specialty merchants typically have more favourable business economics, in terms of unit profit margins and average transaction ticket size.
M-Wallets are more widely used and accepted across all merchant segments, including retail traders such as convenience stores, specialty stores, and service providers like travel and real estate agents. It is important to note here that our study was conducted in January 2017, i.e. two months after demonetization, when there were deep incentives associated with wallet pricing.
ARE MERCHANTS WITH HIGHER PROFIT MARGINS MORE INCLINED TO GO DIGITAL DUE TOŌĆ”
- Type of product/service that caters to a broader consumer mix or has a higher ticket size resulting in more consumer demand to pay digitally?
- Greater ability to defray explicit transaction costs associated with digital payments?
- Lower transaction frequency and longer transaction times which are more congenial for digital payment experiences?
HOW ARE SALES AND PROFIT MARGINS DIFFERENT FOR
Digital Merchants vs Non-digital Merchants
While there isnŌĆÖt much difference in the overall sales, profit margins vary significantly between digital and non-digital merchants.
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
WHAT ARE THE ROADBLOCKS FOR DIGITAL PAYMENTS TO SUSTAIN AND THRIVE?
Cash, still the king of markets!
83% customers of merchants, who currently accept digital payments, prefer transacting using cash. Therefore, significant proportion of customers demanding to pay by cash works as one of the key factors driving merchants to discontinue using digital payments.
Cost optimizations, not cited as reasons for discontinuing usage of digital systems.
Lack of technical support
One of the key obstacles for sustained usage of digital payments by merchants is a lack of awareness on how to report problems merchants encounter while using various digital payment solutions. This highlights the need for more handholding by solution providers, as well as indicates a need to set up robust grievance reddresal mechanisms
Technical support required by merchants
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
WHAT WE LEARNT ABOUT NON-DIGITAL MERCHANTS
TOP 3 REASONS WHY NON-DIGITAL MERCHANTS ARE NOT USING
- Lack of awareness
Of the 539 merchants surveyed, who have not used any digital payment solutions in their businesses, 49% reported a lack of awareness on how to access and use digital payment systems - Low customer preference
26% of merchants stated low customer preference to transact digitally - DonŌĆÖt see the need for digital payments
24% of merchants reported not seeing the need to transact using digital payment modes. This perhaps re-iterates low consumer demand and low merchant awareness on digital payments
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
IS THERE AN INTEREST TOWARDS GETTING INFORMATION AND USING DIGITAL PAYMENTS?
65% of the merchants expressed the interest in learning about and using digital payment systems.
Through our further interactions we learnt that the most effective means to inform merchants is through traditional forms of mass media (e.g., newspaper, radio, etc.). In addition, merchants prefer information tools that can be accessed at all times, and information methods that do not require them to leave their stores.
Merchants are also seen to actively rely on their social networks for information related to business. They tend to approach family members, friends and peers in neighbouring markets for business advice.
Source: Catalyst-IFMR LEAD, Jaipur Needs Assessment Study (2017)
WHAT FACTORS CAN DRIVE MERCHANTS TO SHIFT FROM CASH TO DIGITAL PAYMENT SOLUTION?
Increase in Customer Preference
For merchants, ŌĆ£Customer voice’┐Į? is above any other form of advice, proof, or information relays. Digital payments is no exception to this principle. The study helped us establish that an increase in customersŌĆÖ demand to pay digitally, can play a catalytic role in accelerating adoption of digital payment systems by merchants.
Enhanced Awareness
With close to 50% merchants reporting lack of awareness as the reason for not adopting digital payments, implementing integrated communication programs to enable merchants with requisite knowledge and tools is key to achieving greater adoption. Merchants need to be given information on tangible benefits of accepting digital payments, supported in making informed choices across different solution types, and trained on using solutions chosen. In addition, there is also a need to address merchant apprehensions about security of their money and data, as well as dispel their fear of being cheated. This trust is the cornerstone of new technology adoption.
Attractive Incentives
Tax rebates and rewards offered by the government, as well as the varied types of incentives given by solution providers, are seen as strong influencing factors to drive merchants towards adopting digital payments.
Latest posts by Catalyst Communications Team (see all)
- Decoding JaipurŌĆÖs Digital Payments Landscape - May 15, 2017
Also published on Medium.